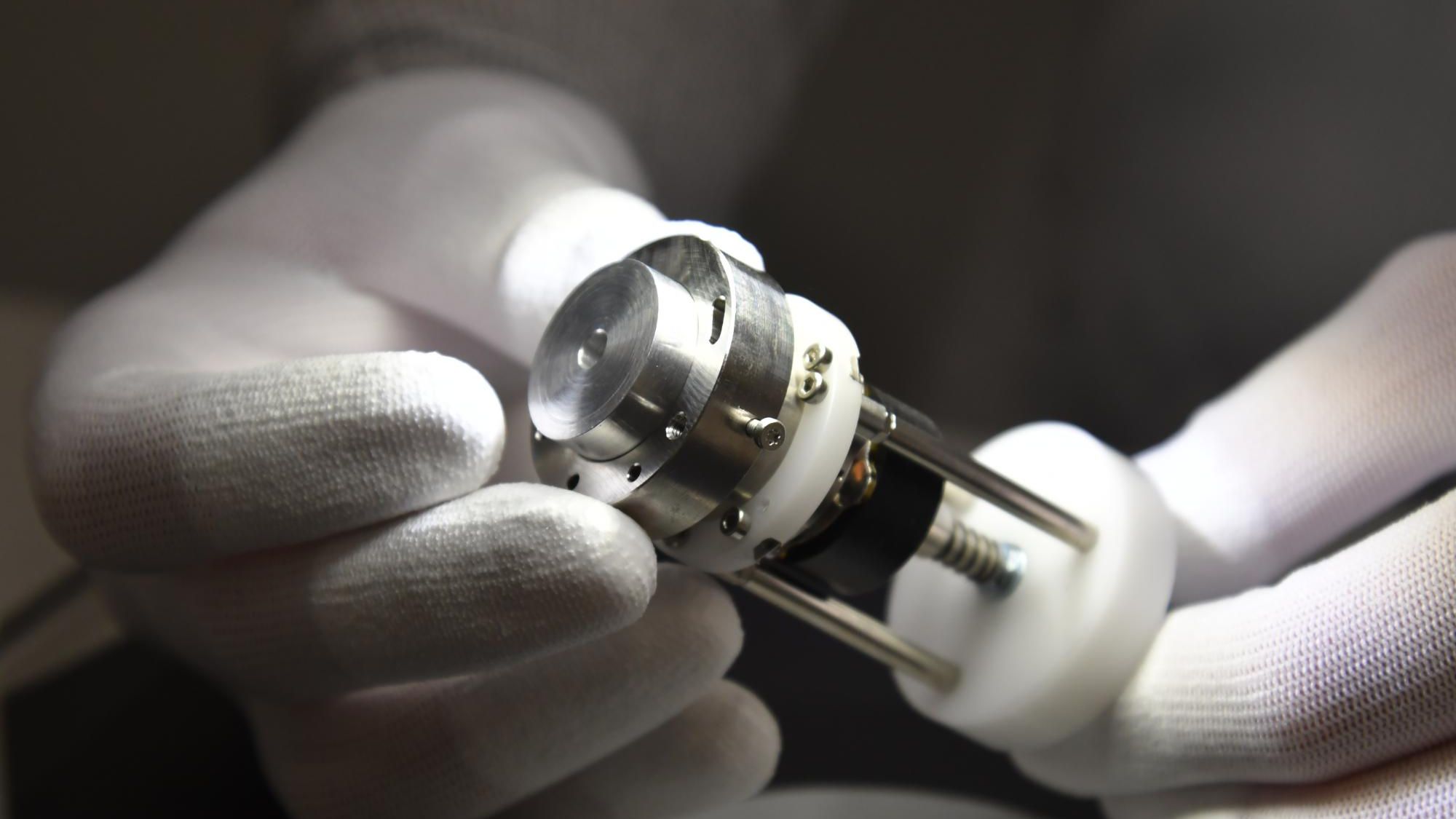
highlights
• tip/tilt range of ±2º (optical)
• closed-loop bandwidth exceeding 1 kHz
• high-efficiency variable-reluctance actuators
• high-resolution, low-power, wide-range eddy-current sensors
• very low power consumption (< 0.2 W) at max. tip/tilt
high resolution, high dynamics.
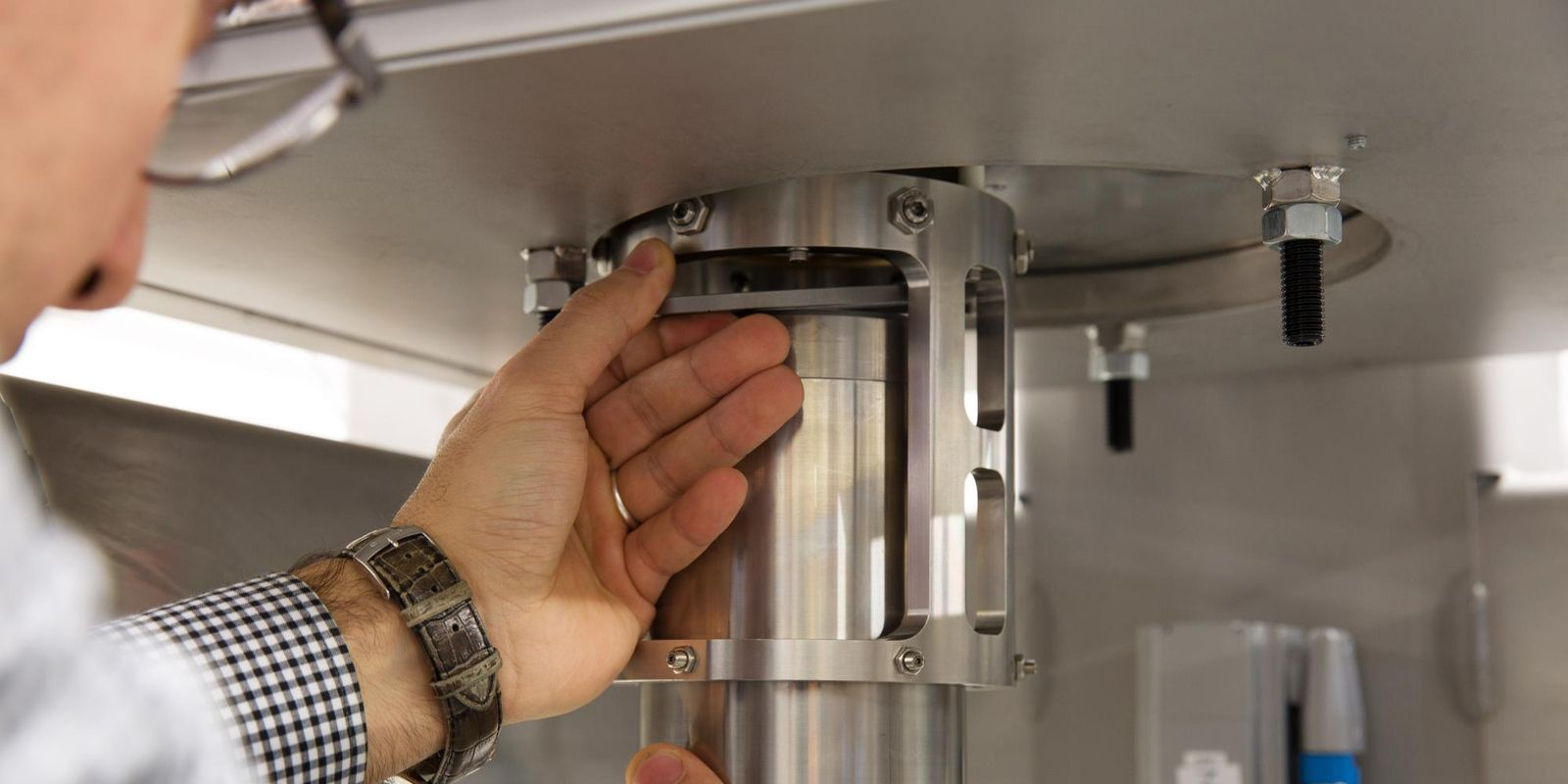
The FSMs in the optical terminals of satellites, airplanes and ground stations provide for the accurate alignment of transmitter and receiver. Their mirror (20 millimetre in diameter) is extremely flat, to prevent wavefront distortion. For the development of a compact, space-compatible FSM, we applied our optomechatronics and manufacturing expertise in close collaboration within the Dutch FSO consortium. The FSM is capable of compensating high-frequency disturbances due to its highly dynamic response mechanism. It features a flexure-based design that enables high linearity and is maintenance-free.
high efficiency, low thermal distortion.
Thermal effects can induce stresses and deformations in the FSM construction. Therefore, we used high-efficiency variable-reluctance actuators, which have a higher force-to-volume and force-to-energy ratio than alternative actuator types. We applied high-resolution eddy-current sensors for accurate pointing precision. An efficient design for manufacturing purposes allows us to produce these FSMs in large numbers.
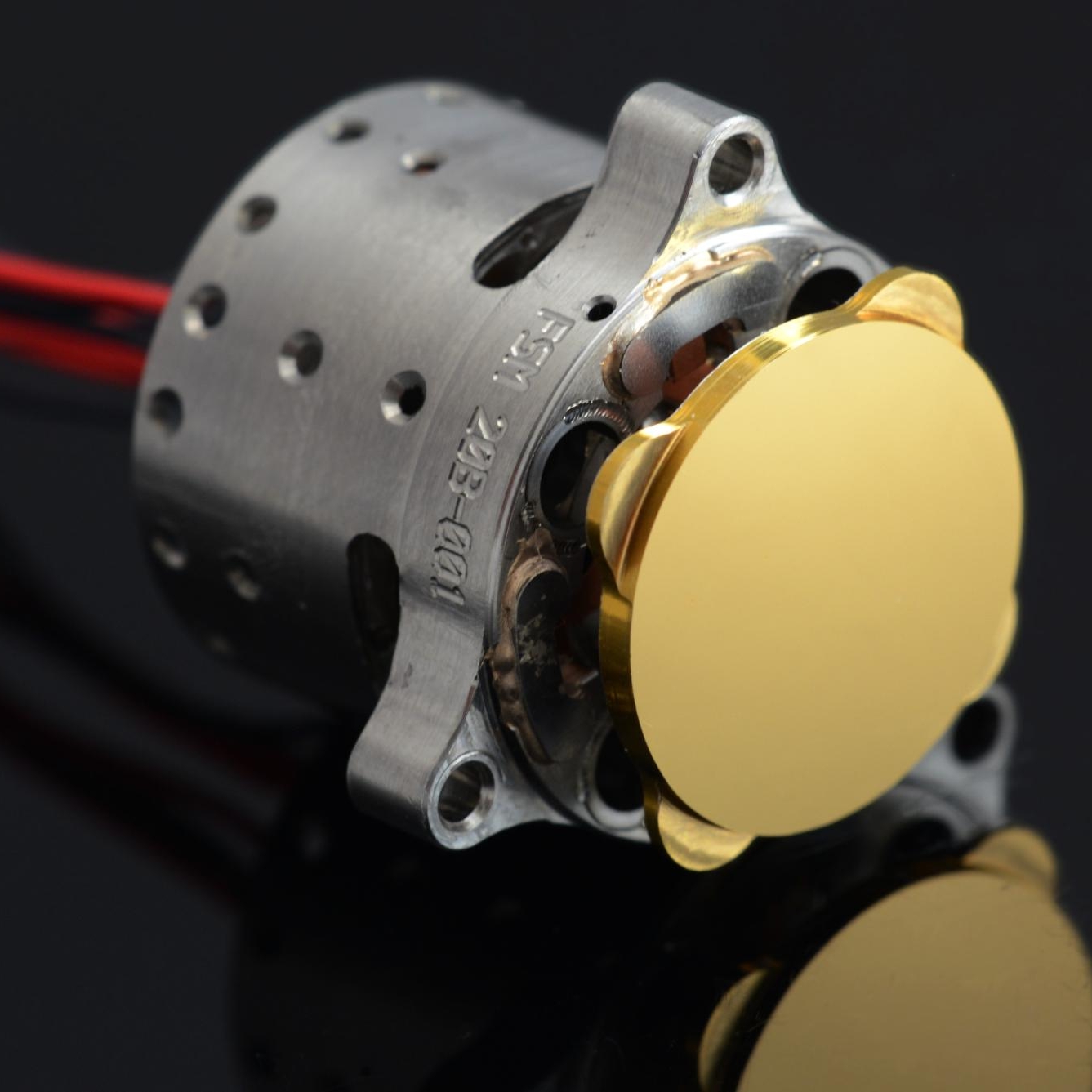

"we successfully industrialized the FSM design."
The FSM’s industrialization presented us with various challenges. We made smart material choices, optimized manufacturability and reduced costs considerably. In addition, we designed special versions of components such as an extremely efficient actuator. We put the FSMs through their paces using strict test protocols, to ensure that they survive a launch and deliver high performance. Our FSMs can be supplied in accordance with the European standards specifications.

more cases & tech insights.
Use cases in machine learning for time series
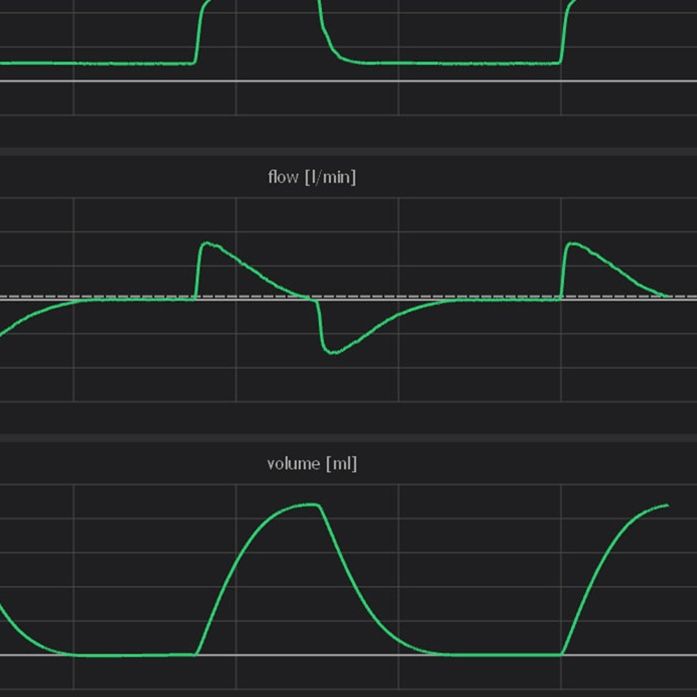
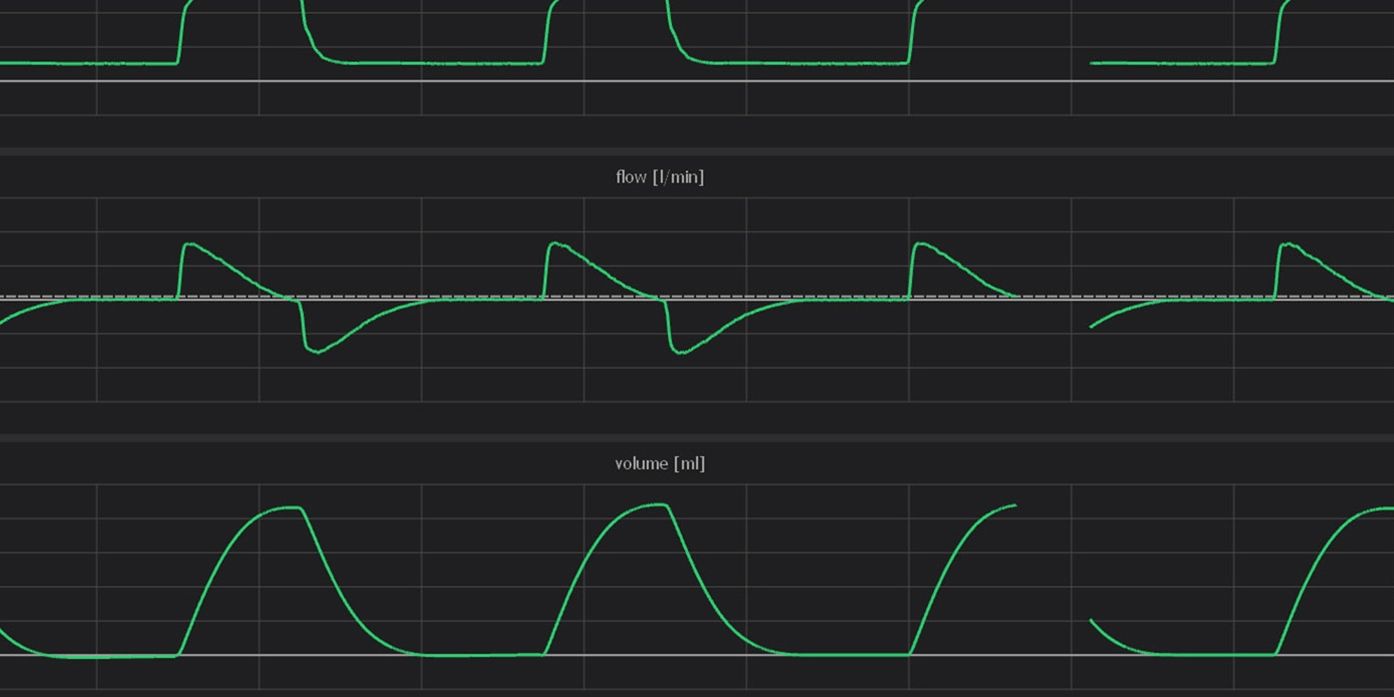
It is essential that the ventilator support is synchronized (in time) with the patient’s spontaneous breaths. A mismatch in this timing is referred to as Patient-Ventilator Asynchrony (PVA). To improve the patient’s comfort and recovery this PVA must be prevented. A key step in this process is the detection and classification of PVA.
Read more

Ice cold stability
In life sciences research, studying cryogenic samples of proteins, viruses and bacteria becomes more and more popular to answer these questions. With Kryoz, Demcon has a cryogenic micro cooler for integration in the electronic microscope on the market.
Read more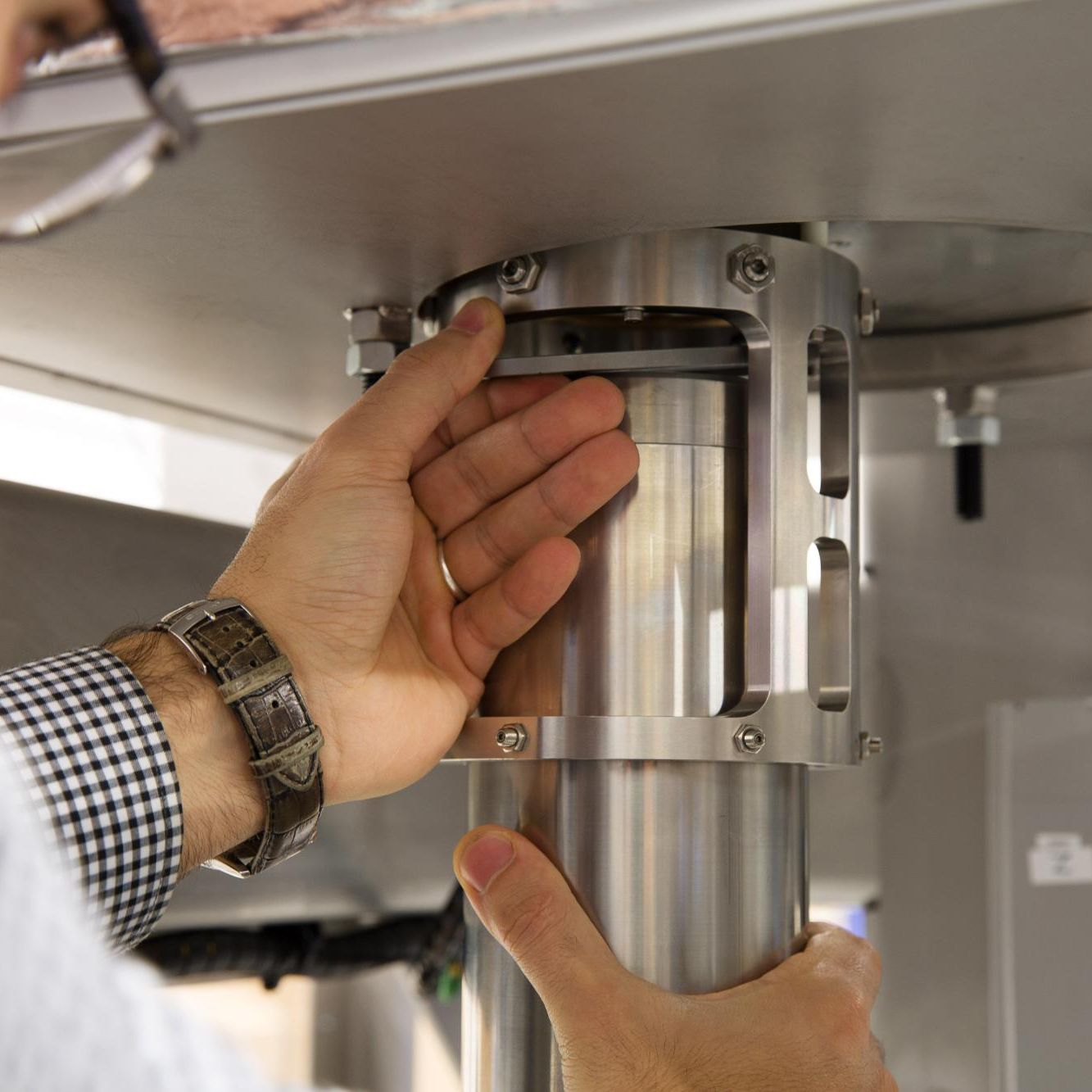

Cracking the glass code
We have grown accustomed to metal and concrete printing. But glass? It not only has a very high melting point, it also becomes brittle after solidifying too quickly. Together with the German specialist in advanced solutions from high-performance materials QSIL we cracked the ‘glass code’.
Read more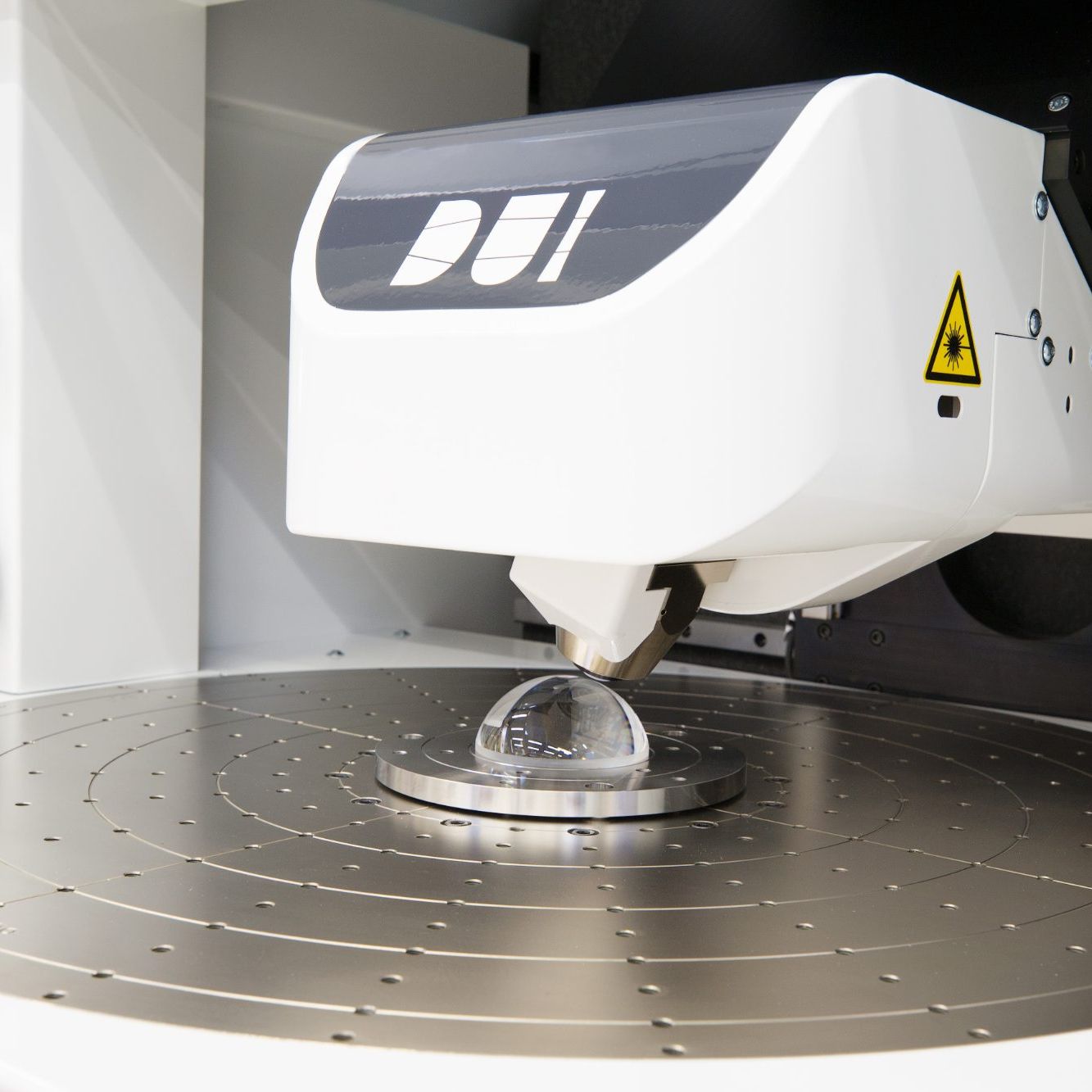
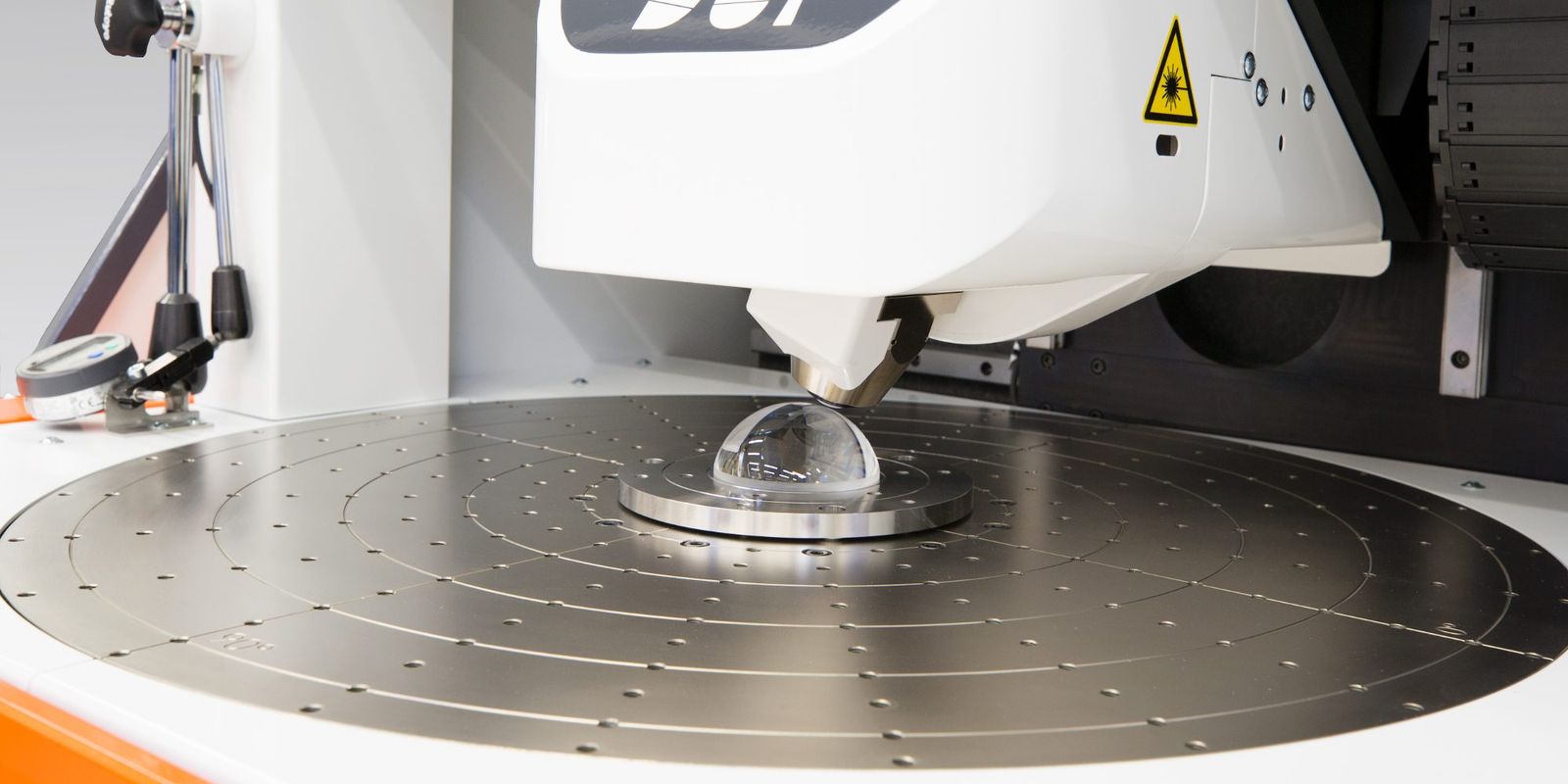

Measuring the nearly unmeasurable
Conventional spherical lenses suffer from spherical aberration. Therefore freeform – often aspherical – lenses have become popular in lithography, aerospace, astronomy and microscopy as well as in (smartphone) photography.
Read more
